Transparency & Blender 3.x+
Table of Contents
While there are some minor updates to the interface, for Blender 3.x how transparent materials are set up and rendered hasn’t changed over previous versions. With this in mind the following is an overview of the different ways to create transparency for both Eevee and Cycles render engines in Blender 3.x+.
Eevee: Principled BSDF Alpha
The simplest transparent material setup is to use Principled BSDF Alpha, the Alpha output [2] from an Image Texture node to the the Alpha input [3] of the primary Principled BSDF node with the materials Blend Mode [1] set to Alpha Blend, Alpha Clip or Alpha Hashed. For this to work images mapped to the linked Image Texture node should include an Alpha Channel.
Important: all Eevee based material transparency requires a Blend Mode to be set in Material Properties. In Settings select Alpha Blend (gradient), Alpha Clip (clip mask) or Alpha Hashed.
For transparency to be rendered in Eevee, in Material Properties [a], under Settings, the Blend Mode [b] needs to be set.
Design note: absent an alpha channelled image being associated with the material it is possible to use the Image Textures Color output [i] by connecting this directly to the Alpha input instead [ii] similar to using an Opacity Mask (see below). Doing this forces transparency to be defined by image colour, which is essentially desaturated to achieve the greyscale tones necessary for masking. Caution should be exercised doing this however, as it may lead to transparency being incorrectly defined.
In the absence of an alpha channel being available it is possible to use the Color output node [1] but in doing this the resulting effect may be incorrect as it is then defined by the colours and not a channel.



Material set up using Principled BSDF Alpha input – the Alpha output of an Image Texture node is connected to Alpha input of Principled BSDF (image must carry an alpha channel).
Eevee: Opacity Map
If the image mapped to a material has no alpha channel transparency can be defined using a separate Opacity Map [4], a greyscale image that’s connected to Principle BSDF’s Alpha input instead. To set this up add a second Image Texture node, load in the image to be used as the mask and connect its Color output [5] to Alpha input [6]. Depending on the Blend Mode set this will then clip or blend as needed.
Design note: images used for opacity masking are generally; black and white for simple clip style masking where transparency defines hard edges and transitions; or greyscale for more complex gradient style blend transparency.
Image left: an example of a typical ‘clip’ style opacity map. Image right: example of an image that produces ‘blend’ or gradient style transparency. Both are colourless greyscale images.



Material set up using a separate Opacity Map to define transparency [4]. So long as the image used to do this is greyscale transparency will be correctly rendered.
Eevee: Transparent BSDF
For more flexible (or complex) transparency the material itself can be set up using a Transparent BSDF node to control the behaviour of the overall material. This can be used where mapped images are not masked using an Opacity Map or Alpha Channel data [7]. To a standard material add a Transparent BSDF [8] and Mix Shader nodes [9]. To each Shader input of the Mix Shader connect the BSDF outputs from Transparent BSDF and Principled BSDF, then link Shader output to the Surface input of Material Output.
Design note: if transparency is primarily defined by an opacity map or alpha channel, the color input of Transparent BSDF [iii], and Fac of the Mix Shader [iv], can be used to modify the characteristics of the effect overall [v] & [vi], useful where a complex material needs to be transparent and not just any image(s) that might be mapped to it, for example fading a transparency effect over time.
Image top: assigning an image with alpha means allows for more finite control over transparency (where specifically and to what degree) [iii] & [iv]. Image bottom: changes made to Transparent BSDF and the Mix Shader change the degree of transparency overall [v] & [vi].



Material set up using a separate Opacity Map to define transparency [4]. So long as the image used to do this is greyscale transparency will be correctly rendered.
Cycles: Principled BSDF Alpha
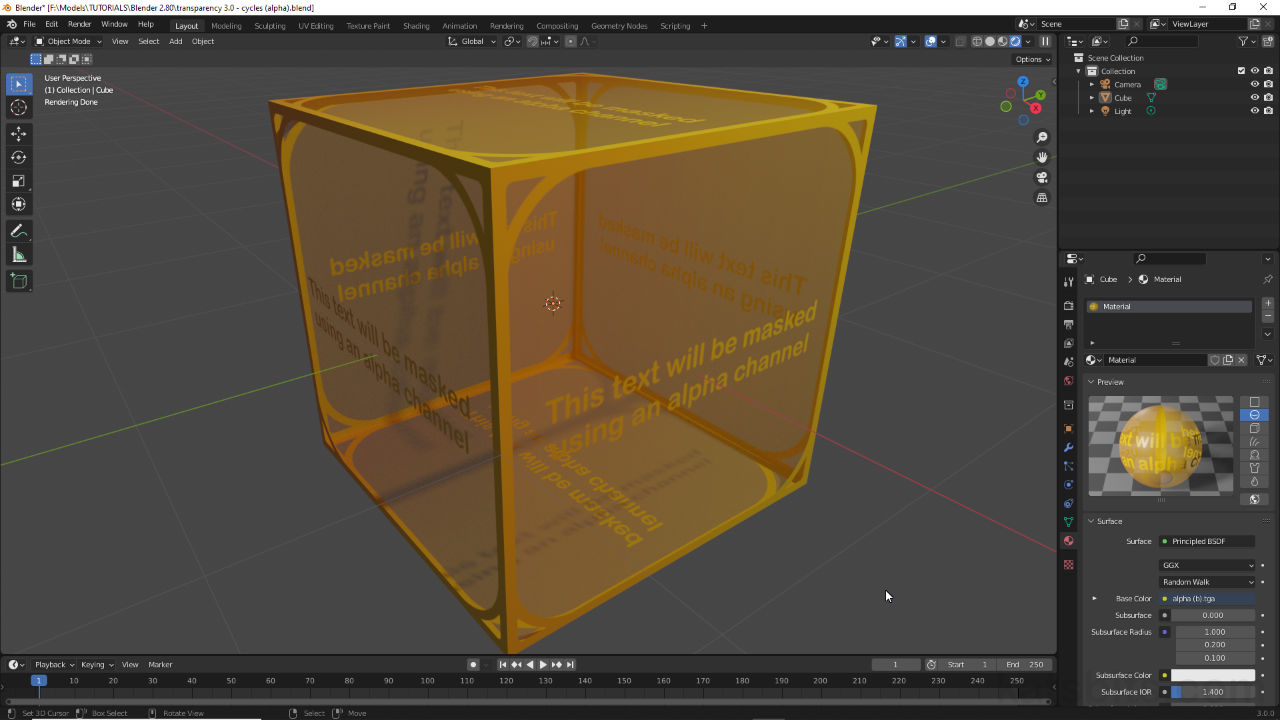
The simplest transparent material for Cycles render engine is to use the Alpha input of Principled BSDF. For this, first drop in an Image Texture node then load in an alpha channel carrying image [10]. Next, link Image Texture nodes Alpha output [13] to Alpha input [14] of Principled BSDF. Finally, make sure Blend Mode [11] is set in Viewport Display of Material Properties.
Important: for Cycles, if Viewport Display is set to Rendered [c], transparency is shown based on the materials node setup, Blend Mode is optional. For Material Preview it must be set..
When Cycles is active and and the 3D Viewport is set to Rendered mode [c] setting a Blend Mode is optional as transparency will be rendered based on the materials node setup.Cycles also displays image based alpha channel and opacity map data automatically if Viewport Shading [vii] is set to Rendered. In other views a Blend Mode [viii] similarly must be set for transparency to be shown in the 3D Viewport. In Material Properties, under Viewport Display options [d], select Alpha Blend, Alpha Clip or Alpha Hashed.
When Cycles is active and the 3D Viewport is set to Material Preview [vii], Blend Mode [viii] must be set for transparency to render else Base Color data is displayed.



The most basic transparent material for Cycles is to link an image [10] with alpha channel [12] to the Alpha input of Principled BSDF [13] and set the Blend Mode in Material Properties [11].
Cycles: Opacity Map
Where a mapped image exclude alpha channel data an Opacity Map can use used to define material transparency in Cycles. Here an extra Image Texture node is used as the link between the greyscale bitmap [14] and the Alpha input of Principled BSDF. For this then drop in another Image Texture node, load in the Opacity Map image then link Color output [15] to Alpha input of Principled BSDF [16]. Ensure Blend Mode is set, to Alpha Clip, Alpha Blend or Alpha Hashed, in Viewport Display options within Material Properties.
Design note: using a separate Opacity Map may be more flexible when setting up transparency as its often quicker to make changes to an image than its alpha channel. It also accommodates situations where alpha channels may not be supported or where content is to be used outside Blender.



Using an Opacity Map to define transparency [14] means using an addition Image Texture node that has its Color output [15] plugged into the Alpha input [16] of Principled BSDF.
Cycles: Transparent BSDF
For more flexible transparency using Cycles a Transparent BSDF node [17] can be used, linked to a Mix Shader [18]. Here, if the mapped image does not include an alpha channel or use a separate opacity map, the materials overall transparency is then controlled by the color input value of Transparent BSDF [19] and/or the Fac input of the Mix Shader [20]. To a standard material add a Transparent BSDF and Mix Shader nodes. Connect the BSDF outputs from both Transparent BSDF and Principled BSDF to the Shader inputs [18] of the Mix Shader. In Viewport Display settings set the Blend Mode to Alpha Blend, Alpha Clip or Alpha Hashed.
Design note: when setting up a transparent material using a Transparent BSDF node, any image based opacity will augment the way the effect is rendered, which can be adjusted using the Color selector of Transparent BSDF [ix] or the Fac value input of the Mix Shader [x] – the former adds colour (tint) to the material, the latter increases/reduces the degree of transparency overall.
Using a Transparency BSDF node to set up transparency also allows the result to be modified based on the Color input setting of Transparent BSDF [ix] and the Fac input of the Mix Shader [x].



Using an Opacity Map to define transparency [14] means using an addition Image Texture node that has its Color output [15] plugged into the Alpha input [16] of Principled BSDF.