Rope & Normal Map Bake
Table of Contents
Making rope in Blender is relative simple when the resulting objects are to be used as is. For normal map baking however, this approach tends to cause problems during render that cannot be resolved due to the way the effect generates the geometry necessary to create the spiral. Instead, a different approach has to be brought to bear that replies on a different type of seed object.
Rope Basics
Ordinarily making a ‘rope’ in Blender is relatively straightforward; 1) add a basic ‘seed’ shape to the Scene in the form of a Mesh Circle [1] – Add » Mesh » Circle, or a Curve Circle [2] – Add » Curve » Circle; 2) assign a Screw modifier [3] – Modifier Properties » Add Modifier » Screw; and 3) change the modifiers Screw [4] property to adjust the wrap or screw behaviour (and Iterations to increase/decrease length); and/or/then optionally 4) adjust the objects rotation in Edit Mode to change the effects orientation relative to the Axis set in the Screw modifier.
Download: Rope texture baking example file;
– KatsBits Rope Normals | c. 1.5 MB (*.blend, *.tga).
Design note: for basic rope making in Blender there isn’t an inherent advantage to using a Mesh over a Curve, or vice versa, as both shapes will generate ‘a (functional) rope’. Choice is then down to what and how the resulting rope is to be used; to bake normal maps for example, either/or is valid.

The two most basic ‘seed’ shapes to make rope, a Mesh Circle [1] and a Curve Circle [2].

Add a Screw [3] modifier from Modifier Properties to the (selected) object.

Adjusting the Screw [4] property to change the shape of the resulting effect (and Iterations to change the length).
Inverted Faces
However, while this approach does create ‘a rope’, when used to bake normal maps, high-resolution to low-resolution, the maps themselves capture the normalised colours [5] incorrectly, which in-turn result in the appearance of artefacts [6] when included in a material, inaccuracies that are due entirely to the way the twist is generated; being extruded along both positive and negative axes of the seed.
Design note: ordinarily it might be possible to compensate for the problem by duplicating the seed object and ‘inverting’ its elements. While this cannot normally be done to mesh based seed objects (vertices cannot normally be ‘inverted’), it can for curves, which duplicates the effect but introduces issues with z-fighting (co-planar surfaces fighting for precedence), which in-turn requires a relatively complex material that forces backface culling in Cycles so only the correct faces are visible. However, doing this does not necessarily exclude backfaces from inclusion when texture baking because hidden faces haven’t been physically removed, they’re not not visible.

Normals baked from a standard modified mesh render incorrectly [5] both to the map capturing the normalised colours, and how that map is then exhibits render artefacts [6] when included in a material.
Inverted Normals
To see this, in Viewport Overlays enable Face Orientation. Here the mesh will be tinted blue or red depending on the orientation of a given surface – BLUE [7] represents OUTSIDE, positive or outward facing surfaces; RED [8],INSIDE, negative or inward facing surfaces. In other words, looking at the twist it’s clear how the shape is being created; both sides of the seed object are extruded and twisted around the same axis, one side effectively inverted and inside-out. For normal map baking this inverts the normals, which in-turn inverts the effect and causes artefacts when rendered. To correct for this the seed object used to generate the rope has to be made a different way.

The twist generated by the Screw modifier extrude along the positive [7] and negative axes of the seed object which essentially inverts one set of faces so they’re inside-out [8], which in-turn inverts the normals captured during Bake.
Rope for Baking
With the above in mind then, the solution to the problem is to change the way the seed object is constructed, it still makes use of a Curve Circle [9] or Mesh Circle [10] as the basis of the rope, but the shape differs; instead of a plain circle the shape is altered to form the basic profile of rope ‘strands’ that can then be extruded using the same Screw modifier [11], this time however, all faces point outwards.
Design note: although faces will now point in the same uniform direction they may still be inverted (the mesh inside-out entirely). To fix this; 1) set a negative Screw value [i] in the modifier, e.g. “-4 m” (negative 4) instead of just “4 m” (positive 4); or 2) physically invert the seed object; for a Curve Circle select the all node segments in Edit Mode and from the Segments [ii] menu click Switch Direction [iii] – Segments » Switch Direction; for a Mesh Circle, in Edit Mode select all vertices then using the Rotate tool [iv] flip the selection 180 degrees around the appropriate, single, axis, e.g. rotate 180° around the X axis – R » X » 1, 8, 0. In both instances this (re)inverts the extruded surfaces, which then point outwards.
Setting a negative Screw value [i] ‘inverts’ the resulting mesh – faces there were pointing inwards are flipped to face outwards.
Alternatively the seed object can be edited directly – for Curve Circles objects [ii] use Switch Direction [iii] in Edit Mode to invert segment nodes, which in-turn inverts faces…
… for Mesh Circles, in Edit Mode use the Rotate tool [iv] to ‘invert’ the object along a single axis by 180 degrees.

In Edit Mode for both Curve Circle [9] and Mesh Circle [10] objects, edit the vertices (mesh) or control points (curve) appropriately to change the profile of the seed…

… then assign the Screw modifier [11] and change the Screw value to shape the rope.
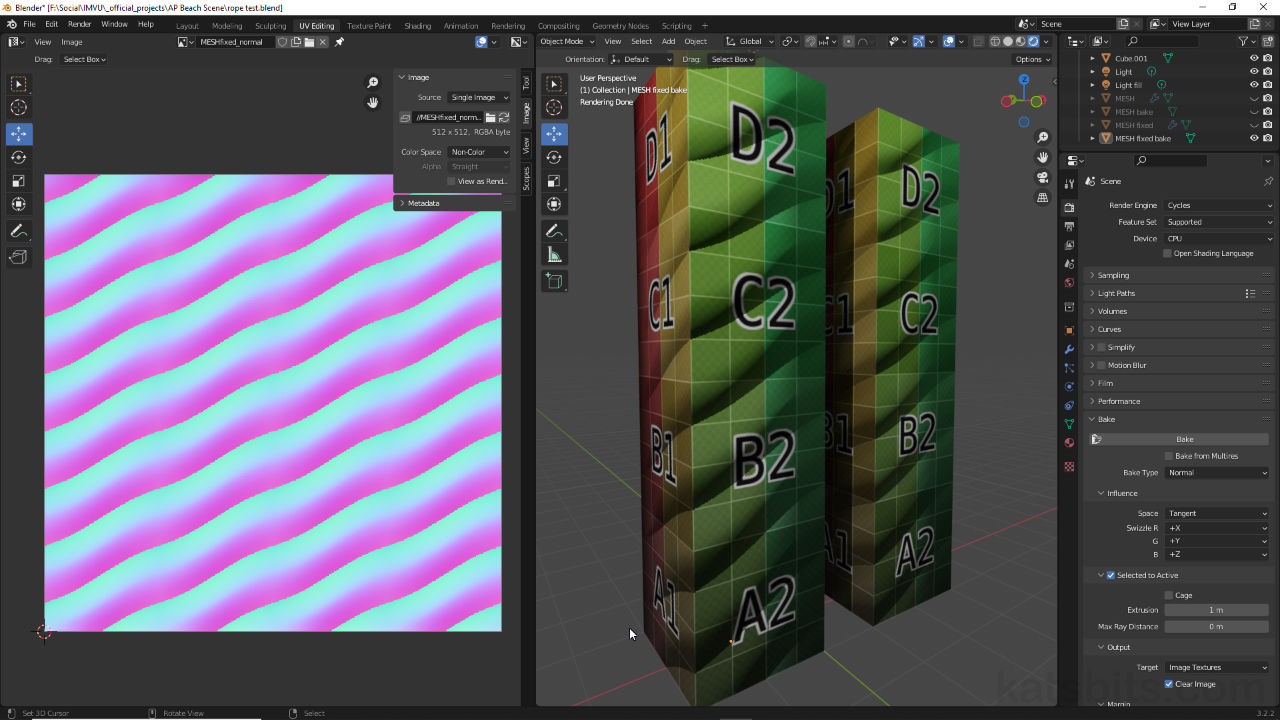
Bake Rope Normal Maps
Once the rope section has been generated it can be baked as normal; a low resolution mesh must be appropriately UV unwrapped and mapped with material set up to utilise normal maps. Both ensure the correct transfer of high-resolution mesh data. Switch to Cycles to access Bake properties and set Normal as the Bake Type. Select the high, then low resolution versions of the object and click the Bake button. Using the altered seed object the rope will then bake correctly without artefacts.

After altering the seed object normal maps can be baked without artefacts or incorrect colour inclusion.